“Sleep When Your Baby Sleeps” – Planning for Newborn Sleep Bliss
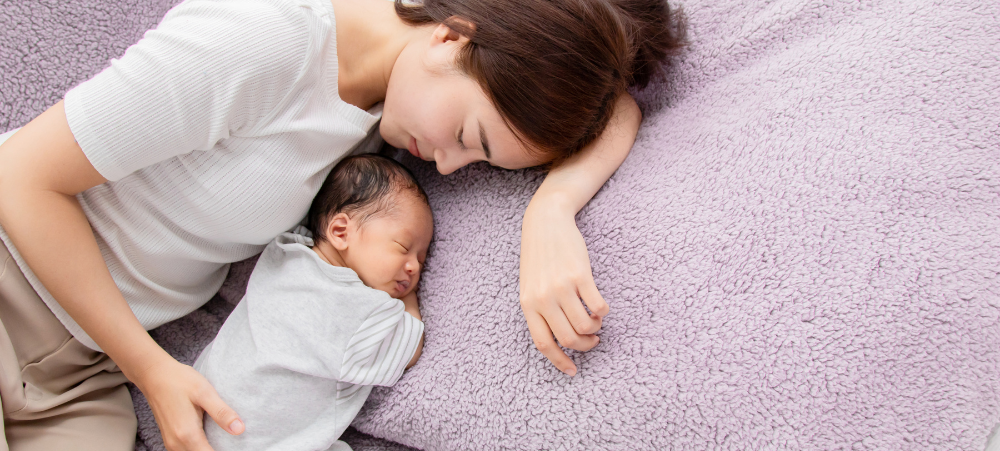
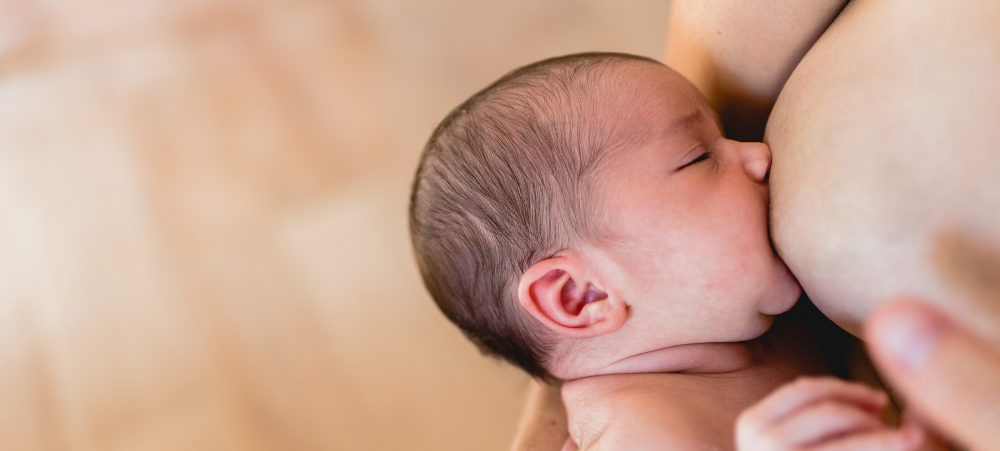
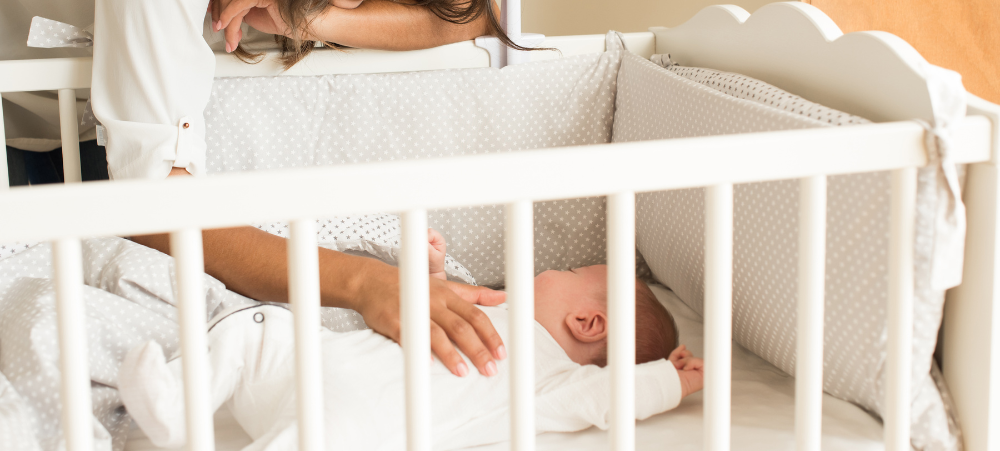
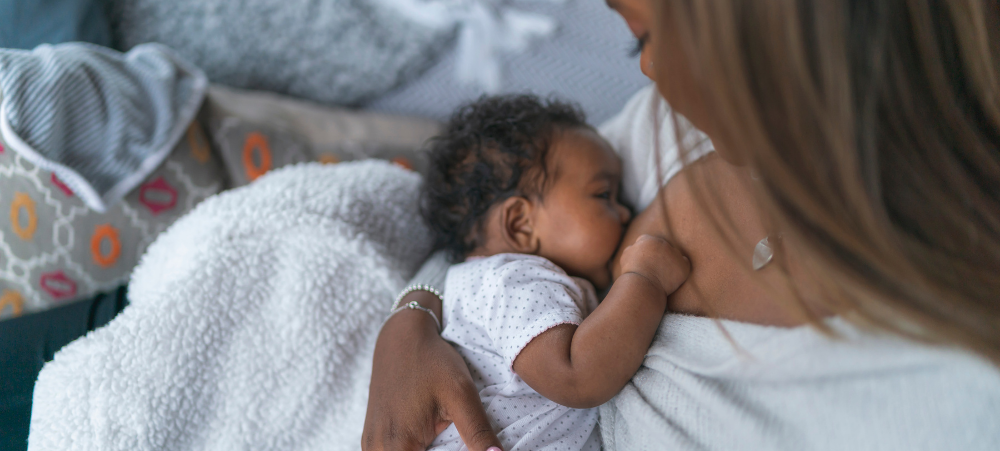
I am the mother of two beautiful boys and have experienced two polar opposite newborn phases; one pure undisturbed bliss (even with a three-year old running around) and the other where the wheels completely fell off around eight weeks postpartum. After my first, very wobbly experience, I am here to share how I fought for and set myself up for the most wonderful, enjoyable, relaxing and sleep-filled (yes, I really am using those words!) postpartum with my little Leo, our baby lion (named by my firstborn, Max). Both my babies were born into my arms at home, in births I had manifested and dreamed of. I won’t go into too much detail about what I did wrong when Max was brand new. But as a first-time mom, most of it was due to being uninformed, taking bad advice, not listening to my intuition and not giving myself, the most important part of the mother-baby dyad, the care, quiet and nurturing I needed to look after my tiny newborn. I have since learned that our babies and children feed directly from our nervous systems; they physically need us to regulate themselves. I knew that with Leo I had to plan very carefully and put the necessary support, boundaries and expectations from those around me in place very securely before he was born to allow myself the space and time I needed to be able to stay in a calm, happy, ventral vagal state while having a newborn in my arms and a three‑year-old to tend to as well. I knew that this would mean that my newborn would be calm and happy too, as he was feeding off my nervous system. So, for me, there were a few very important things I planned so I could rest and sleep once he was born: I made sure that my three-year-old would be looked after and his needs met by my parents during the day. I still did his bedtime every night, even the day Leo was born, which is a blessing one has when birthing at home. I made sure my fridge was stocked with all the right postpartum foods to help nourish me after birth and give me all the energy I needed to establish breastfeeding. A great book I read was The First Forty Days: The Essential Art of Nourishing the New Mother by Heng Ou with Amely Greeven and Marisa Belger. I followed a forty-day confinement/resting period after giving birth, where I stayed in my home for this special time. I didn’t leave my bedroom for the first seven days and slowly made my way into the rest of the house only when I felt I was ready. This tradition is followed in many cultures; however, in our own fast-paced Western culture, it has been largely overlooked. In my opinion, this is why so many mothers have difficult newborn phases filled with the social pressure to get back to normal life way too quickly. All they should be doing is looking after their baby while others care for them. Some of you reading this may be thinking, how the hell would I even do that? And that is why I said I had to ‘fight’ for my postpartum bliss. It doesn’t just happen, I promise you! I took a Chinese herb called Calm Shen and an incredible amino acid called L‑theanine, which I wish more mothers knew about. These aided me in restful sleep and calming the anxious mind, so I found it easy to drift back to sleep at night after feeding and to lay down for a nap with my baby and actually sleep. I made sure I lay down to rest and sleep whenever Leo was napping. Because I felt so calm, so held by those around me and so safe, I was actually able to nap with my teeny one in my arms and not just lay there wide eyed and wired, wondering if he would wake up the next time he stirred. I also became very comfortable with newborn active sleep patterns, where they are fast asleep but moving around and making noise like crazy (enter me sleeping with ear plugs day and night!). With Max, I used to jump up to rock and feed him the moment he moved, which meant that most of the time, I was actually waking him up and being the reason for his short naps and poor nighttime sleep. I went to bed super early. Now when I say early, I mean like 7:30 pm, latest 8:00 pm. My three-year-old goes to bed at 6:00 pm and sleeps through the night, so Leo and I would follow close after him. This meant I had 12 hours in which to get as much sleep as I could, taking the edge off feeling anxious about how much sleep I got. For most nights, this ended up being a good eight hours for me (obviously interrupted by feeding). BLISS! I used a Love to Dream swaddle, Sleepyhead pod, soft white noise and a Lulla Doll as a lovey from day one and made sure there was some light for our day naps and that nighttime was completely dark. For the first 16 weeks, I co-slept with Leo and had him next to me either in my arms or in a co-sleeper. I mastered the art of breastfeeding while side-laying, which meant I often fell asleep while feeding him. This was another way we had our long blissful naps during the day, always laying together. Something I used to dread with Max became something I truly miss now that Leo is eight months old and sleeping happily through the night in his own room. I seriously loved my postpartum journey, from my empowering one-hour-long unassisted homebirth in our beautiful new home by the sea in Cape St Francis (where the midwives arrived five minutes before he was born – but that’s a story for another day!) to my dreamy newborn cuddles and sleep-filled days and