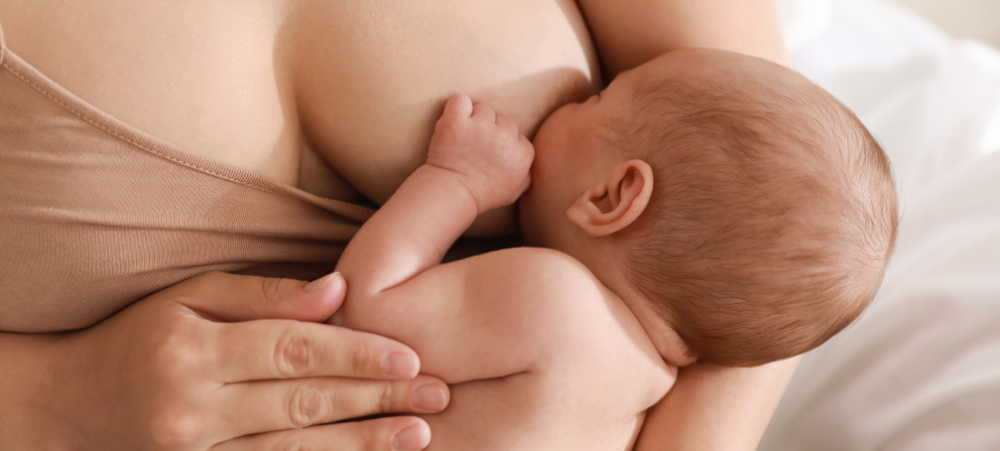
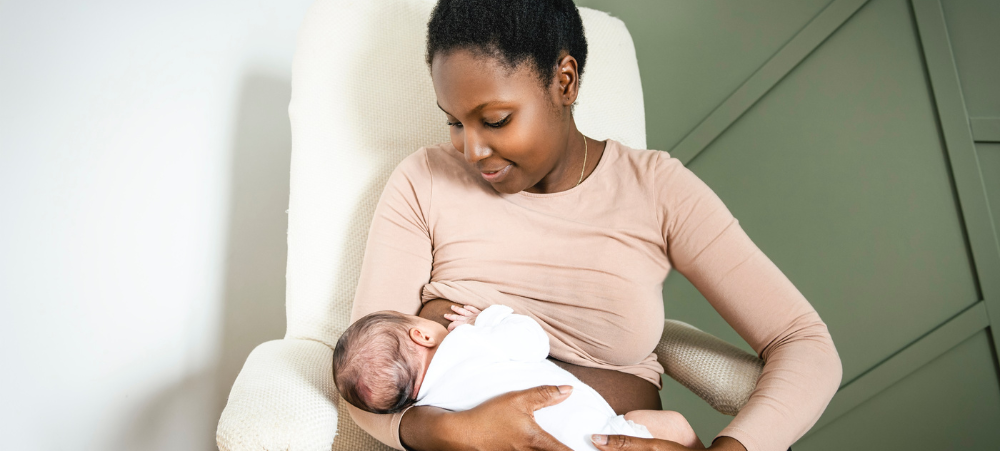
South Africa is one of the most unequal countries in the world, and this is tragically evident in the nutritional status of millions of our children. However, breastfeeding has the power to be an equaliser ensuring that no child is left behind when it comes to optimal health and development. Despite widespread promotion of the many benefits of breastfeeding, these rates remain low in South Africa. The country has solid policies in place and progressive legislation for infant and young child nutrition, although these are not often implemented and monitored consistently and effectively. Perhaps, though more critically, there’s a lack of a groundswell of support for all breastfeeding moms in our homes, workplaces and communities. According to the World Health Organisation (WHO) guidelines for maternal and infant health, babies should be breastfed exclusively for the first 6 months of life. After that mothers are encouraged to breastfeed on an ongoing basis as solid foods are gradually introduced from six months. The evidence-based health benefits are clear – improved maternal and child health, reduced household food costs, reduced national healthcare costs and improved child well-being and development. There are a range of reasons why mothers either do not start breastfeeding or give it up prematurely. Sometimes, there are medical reasons that cannot be prevented. But mostly, moms experience barriers and obstacles that they cannot overcome on their own and they do not get the right support at the right time. Spokesperson for the Association for Dietetics in South Africa (ADSA) , Tsholofelo Mohloane, a Registered Dietitian and Lactation Consultant says, “I do much of my work at a public hospital and I am always encountering mothers who struggle with solvable issues such as perceived low breast milk supply, sore nipples, engorged breasts, improper breastfeeding positions and little to no knowledge of the importance and benefits of breastfeeding, leading to mothers opting for breastmilk substitutes. So, we must address the lack of educated support for breastfeeding moms in the healthcare system, especially for women in under-resourced communities. However, the issue is much wider than this. There’s also a lack of support for breastfeeding in homes, families and communities. While workplaces have policies in place to support breastfeeding mothers who have returned to work, reports of women resorting to expressing milk in their cars or toilet cubicles during lunch breaks highlight a lack of adequate support. Failure to provide clean, private facilities and adhere to legal requirements for additional breaks undermines these policies and can discourage breastfeeding mothers from continuing. Employers must ensure they fulfil their obligations to create a supportive environment that enables all breastfeeding employees to express milk comfortably and safely. It is a clear lack of support when employers do not make facilities available and fail to adhere to the legal guidance to provide breastfeeding workers additional breaks every day to express milk. In broader society, there are judgements made, and moms are frequently shamed for needing to feed anywhere, any time. All of this can be tremendously discouraging and stressful for a new mom, and moms sometimes feel that there is no other option than to bottle-feed with commercial milk formula. But in terms of health, child development and healthcare costs, we pay a high price as a country for failing to wholeheartedly support and encourage all our breastfeeding moms.” World Breastfeeding Week is celebrated every year from 1 to 7 August. In 2024, the theme is Closing the Gap: Breastfeeding Support for All. ADSA spokesperson, Professor Lisanne du Plessis, a leading academic from Stellenbosch University focused on Public Health and Community Nutrition sets some of the key campaign messages in a South African context: Support for women to breastfeed anytime, anywhere, so that it is normalised and not censured in public life – “In my opinion, the barriers to breastfeeding are not cultural issues, but societal,” says Prof du Plessis. “This includes unsupportive workplaces and public spaces, lack of or poorly implemented maternity protection policies, ignorance about correct breastfeeding practices, lack of access to lactation support and social perceptions about women’s roles. Mothers need to be supported to nourish and nurture their babies, and their partners, own mothers, mothers-in-law, grandmothers and the broader family and community should be educated on how to support breastfeeding mothers and about the dangers of introducing commercial milk formula unnecessarily.” Effective maternity entitlements that do not force women to choose between their families and their work – “For South Africa the changes I would advocate for here include a breastfeeding policy in every workplace. This can ensure that the necessary sensitisation is created about mothers’ needs and employers’ human resource obligations. Provision of a private, hygienic space to breastfeed or express, and the resources to safely store breastmilk are essential in every workplace. The provision of educational material or access to a professional breastfeeding consultant can create the necessary support for mothers to ensure continued breastfeeding once they have returned to work.” An end to exploitative baby-milk promotions in all contexts – “The Lancet Series on Breastfeeding of 2023 explicitly shows that commercial milk formula companies use perverse and exploitive marketing and promotional methods to drive the demand for their products. These tactics continue to undermine breastfeeding and contribute to millions of women not breastfeeding as recommended, which results in infant and young child illness and death. The Global Nutrition report of 2018 stated that just 35 of 194 countries have laws to cover all areas of commercial infant formula, while a further 96 are partially covered. Despite some efforts to stop the harmful promotion of commercial milk formula, countries are still falling short in protecting parents from misleading information. South Africa has progressive legislation to curb the promotion and marketing of commercial milk formula through Regulation 991. However, the capacities to enforce the law and follow-through on transgressions are limited. Many of these offences are also subtle and happen online, where it is difficult to monitor. The current loopholes that industry has found in SA Regulation 991 should be amended and more