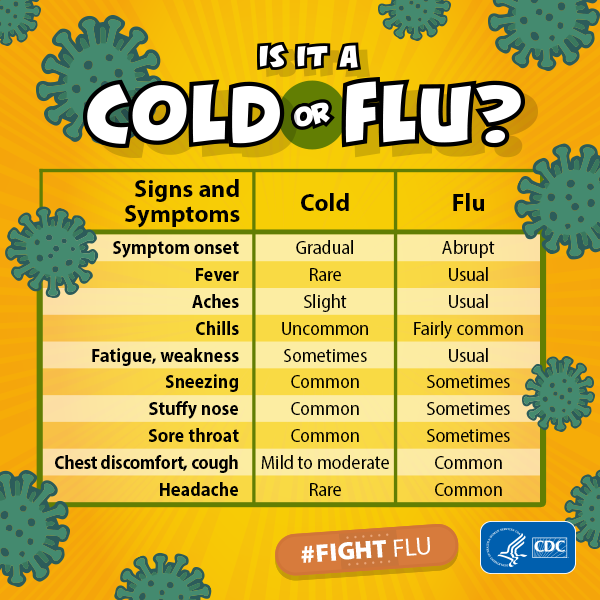
Winter is here and so are coughs, colds and flu. Common colds and flu are both caused by viruses and share many of the same symptoms however colds are usually milder and do not cause any serious complications. More than 200 viruses can cause a cold whereas the flu is caused by the Influenza virus. This is why there is no vaccine available for the common cold.
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE?
Generally colds affect you from the neck up where the flu attacks your entire body. A cold causes a runny or blocked nose and sneezing. There may be a sore throat with a slight headache because of nasal congestion. A cough can develop but this is mostly because of a post-nasal drip. Cold symptoms usually last for about a week. If the symptoms do not improve after a week it is less likely to be a cold and an allergy or sinusitis should be considered.
The flu on the other hand causes more distressing symptoms. These include fever, chills, body aches, cough, weakness and extreme tiredness in addition to all the symptoms of a cold. Most flu symotoms also improve after a week but it is common to still feel a little weak and tired for up to two weeks.
Pneumonia is a complication of the flu, especially in the young, elderly and those with pre-existing chronic diseases. If your child seems to be getting worse, has difficulty breathing, is extremely lethargic or irritable, is refusing to take in enough fluids and/or has a persistently high fever you need to seek medical assistance.
HOW TO REDUCE THE RISK OF CATCHING A COLD OR THE FLU
- Vaccinate: make sure everyone in your family gets the seasonal flu vaccine every year. It takes about two weeks for antibodies to develop and offer protection. It is recommended you receive the flu vaccine before the flu season starts but it’s never too late. In South Africa the flu season usually starts around the first week of June but in previous years it has started as early as April.
- Hand washing: Make sure you wash your hands frequently and teach your children about good hand washing. Wash with warm soapywater for at least 20 seconds. Cold and flu viruses enter the body through the mucous membranes of the nose, mouth and eyes. This means that every time you touch these parts of your body with hands that have the virus you have a high risk of infecting yourself.
- Cover up: teach your children to sneeze or cough into a tissue or their elbow and NOT into their hands.
TREATING A COLD OR THE FLU
Antibiotics do not work against viruses. Therefore they will not work for a cold or the flu unless a bacterial complication has developed. Often I see that antibiotics are prescribed for viral infections to “treat” the parents rather than the children. This is dangerous and will only lead to the emergence of more antibiotic resistance, which is already a major global problem. Some parents will argue and say that their child started recovering after a few days on antibiotics but this is probably because the viral infection has run its course and is coming to an end instead.
There are plenty of over the counter (OTC) medicines available for cold and flu symptoms targeting both adults and children. However, these are not recommended for use in children under two years of age. Some experts even suggest avoiding them up to six years. There is very little evidence to prove that these medications work at all and some of them can cause serious side effects in younger children such as hallucinations, irritability, restlessness and abnormal heart rhythms. More importantly codeine, which is an ingredient commonly found in cough, cold and flu medications should not be given to children younger than 18 years of age.
There are some antiviral medicines available for the flu. These are typically prescribed to children at high risk of complications, such as children with asthma. These drugs work best if taken within 48 hours of the onset of symptoms and help by reducing the length and severity of the infection.
Unfortunately, there is no cure for the common cold and flu. It will usually clear up on its own and all you need to do is treat it symptomatically:
Analgesics and antipyretics: you can give your child paracetamol or ibuprofen, NEVER aspirin. To find out more about medicines for pain and fever in children you can read my previous blog: https://www.oneaid.co.za/medications-for-pain-fever-in-children/
Fluids: make sure to give your child lots of fluids to prevent dehydration especially if they have a fever and/or are refusing to eat.
Rest, rest and more rest: allow your child to rest. The body needs rest to recover so keep your child home from school and forget about extra murals for a while.
Nose sprays: the most important nose spray you should use is a saline spray. These help thin the mucus and reduce nasal congestion. There are also other decongestant nose sprays that can be used in older children.
Warm steam and humidifiers: sitting in a steamy bathroom or using a humidifier, which adds moisture to the room, can help loosen mucus in the nose and relieve coughing.
TOP 5 COLD AND FLU MYTHS
- Milk and other dairy products make a cold worse
There is no evidence that dairy products increase mucus production. - “Feed a cold, starve a fever”
If your child have a fever they need more fluids. Fevers cause dehydration and this happens more rapidly in young children. Provide plenty of fluids when your child is sick and if he or she has an appetite, allow them to eat. - The flu vaccine will give you the flu
The flu vaccine is made from an inactivated virus so you cannot get the infection. People who do get sick after receiving the vaccine got the infection from another source and were going to get sick anyways. Also, some people develop flu-like symptoms after a vaccine. This is a normal immune response to a vaccine. These symptoms never last as long as the flu would. - You can catch a cold or the flu by going outside in cold weather without a jacket, having wet hair in winter or walking barefoot
Germs make you sick and not the cold. People make this natural association because the cold and flu season happens during winter. The reason for this is that in colder weather people tend to congregate closer together to keep warm and doors and windows stay closed. This allows viruses to spread more easily. - Chicken soup will make you better
There are no antiviral properties in chicken soup but it can definitely make one feel better. The warm liquid can soothe a sore throat and keep you hydrated and the steam can help break down nasal congestion and reduce stuffiness.
It’s quite common for children under two to have as many as 8-10 colds a year with prescholars getting around 7-8. It takes years to develop an immunity to viruses and since there are more than 200 viruses that can cause a cold the high rate of infection in our little ones makes sense. Don’t despair, the cold and flu season does eventually end but for now it’s a great reason to give more healing cuddles and keep our little ones loved up and warm this winter.
RESOURCES
https://www.cdc.gov/flu/symptoms/coldflu.htm
https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/when-give-kids-medicine-coughs-and-colds
https://www.health.harvard.edu/diseases-and-conditions/10-flu-myths
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2722603/
- How Safe Are Teething Gels? - November 19, 2025
- 10 Essential Tips To Prevent Poisoning In Your Home - October 29, 2024
- A Bump To The Head: When Should You Worry? - October 25, 2024





