What Is Down’s syndrome
- A Genetic condition that causes mild to serious physical and mental problems
- Extra chromosome (21)
- Three types:
- Trisomy 21 (every cell has an extra copy of chromosome 21)
- Translocation downs syndrome (Each cell has a part of chromosome 21 attached to another chromosome)
- Mosaic downs syndrome (only some of the cells carry an extra chromosome)
Presentation of Down’s Syndrome
Common physical signs
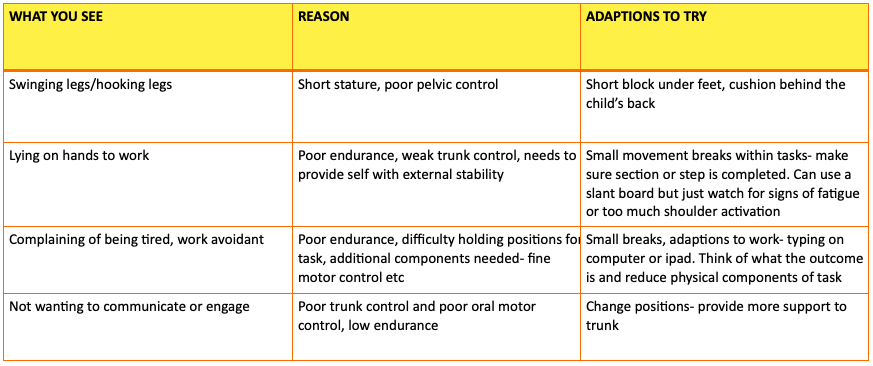
- Decreased muscle tone at birth
- Difficulty with endurance in ALL activities
- Poor ability to assume and maintain positions
- Excess skin at the nape of the neck
- Flattened nose
- Separated joints between the bones of the skull (sutures)
- Single crease in the palm of the hand
- Makes fine motor activities more difficult
- Difficulty assuming and holding various pinches – fatigue easily
- Small ears
- Small mouth
- Upward slanting eyes
- Wide, short hands with short fingers
- White spots on the coloured part of the eye (Brushfield spots)
- Cognitive impact
- Mild to moderate cognitive delay
- Hearing difficulties
- Cardiac problems – regular check ups with a cardiologist – 50% of children present with a cardiac defect
- Visual difficulties – squint, cataracts, crossed eyes, visual processing difficulties, difficulties with eye movements due to low tone in the optic muscles (60 – 80%) Bull et al. (2022)
- Visual difficulties impact the processing and output during class activities
- Can impact playground engagement
- Impacts gross motor skills and praxis
Essentials for managing Down’s syndrome:
- Early intervention
- Physiotherapy /Occupational Therapy /Psychosocial intervention
- Environmental adaptions and modifications
- IEP’s, job training and independence in Activities of daily living
Areas of focus:
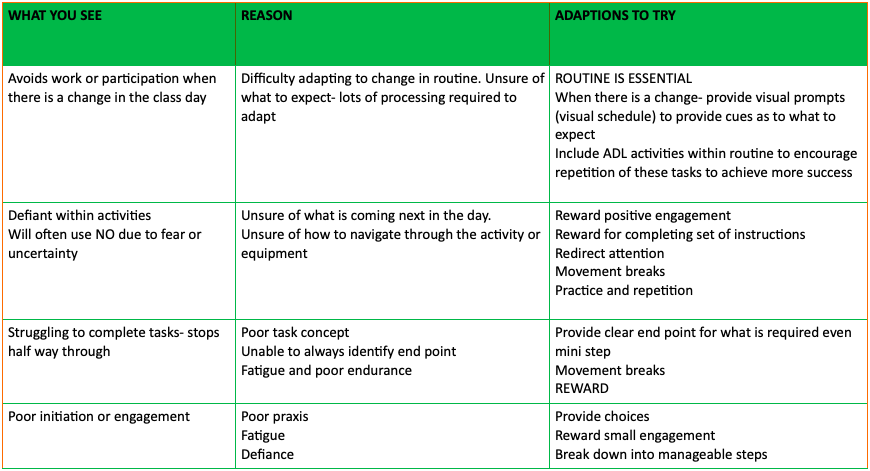
- Postural control
- Visual Difficulties
- Behaviour
- Classroom adaptations
1. Postural Control:
Important referrals for Postural control:
- Physiotherapist
- Speech therapist
- Occupational Therapist
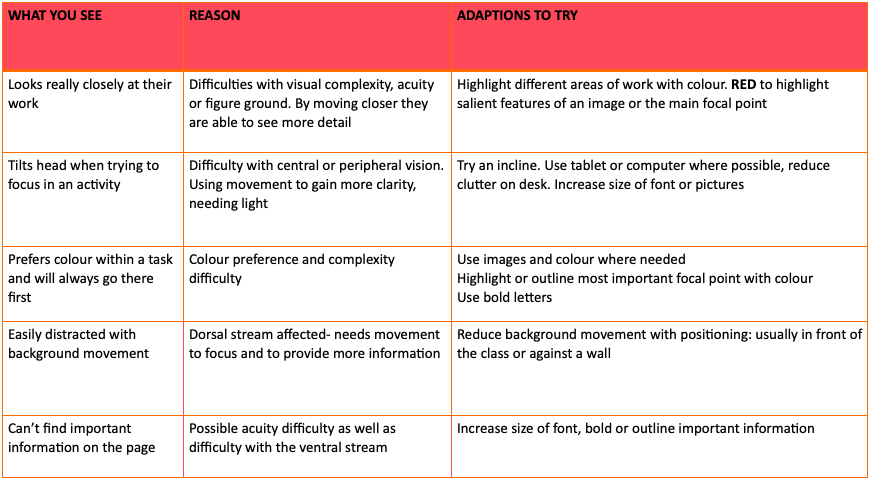
2. Visual Difficulties
Presentation of visual difficulties:
Refractive errors:
- Hyperopia (far sightedness)
- Myopia (near sightedness)
- Astigmatism (blurry vision)
Visual acuity difficulties:
- Blurry vision, difficulty with seeing detail
Kerataconus:
- Difficulty with close work- out of focus
- Better with contacts- difficult for children to use the contacts
Cataracts:
- Essential early detection
- Clear image is not presented to the child in the correct way: visual learning is affected
Nystagmus:
- involuntary side-to-side, up and down, or circular movement of the eyes
- May disappear by itself
Cortical visual impairment
- Colour preference (red and yellow, borders) – can use colour as an anchor and to assist with recognising detail in an image
- Need for movement to focus
- Visual latency
- Visual field preferences
- Difficulties with visual complexity
- Need for light
- Difficulty with visual focus in the distance
- Atypical visual reflexes
- Difficulties with visual novelty – look for familiarity
- Absence of visually guided reach – affects praxis (automatic reach)
Important referrals for Visual Difficulties
- Functional/behavioural visual specialist
- Ophthalmologist
- Occupational Therapist
3. Behaviour
Very Common
- 2 in 3 children with Down’s syndrome have difficulty with managing their own behaviour
Reasons:
- Difficulty controlling impulses
- Trouble communicating needs
- Difficulty with judging social environments and settings –
- Sometimes play too rough
- Trying to figure out play equipment so tend to grab or occupy certain play items
- Difficulty sharing
- POOR work endurance
- Defiance
Important Referrals:
- Psychologist
- Speech Therapist
- Occupational Therapist
4. Classroom Adaptations:
Difficulty with executive function skills
- Money Management
- Time management
- Task evaluation
- Working memory
- Impulse control
Toileting difficulties – either from awareness, emotional response or physical difficulty with the task
Delay in milestones
Difficulty retaining information: REPETITION NB

Written by: Nicky Forssman
Glenoaks is a private remedial and special needs school in Johannesburg that unleashes potential!We nurture academic, functional, social and emotional growth for learners and personalize support according to the needs and strengths of each learner. We create a nurturing and inclusive environment for our learners which is supported by our dedicated, passionate and professional team. We achieve this through innovative adaptation, accommodation, differentiation and individualisation for each learner.
Latest posts by Glenoaks Remedial and Special Needs School (see all)
- When to Push My Child and When to Step Back - March 18, 2024
- Benefits of Including STEM into the Classroom - March 5, 2024
- The Role of Parents in the Education of Special Needs Children and Fostering a Collaborative Approach - February 21, 2024
Post Views: 35,727